This security bulletin written with support from Ordr senior product manager Derek Loomis
Google Chrome has experienced eight zero-day exploits so far in 2024 and four in May alone! To mitigate these threats users are strongly advised to update their Chrome browser to version 125.0.6422.112/.113 for Windows and macOS, and version 125.0.6422.112 for Linux.
Similarly, users of Chromium-based browsers such as Microsoft Edge, Brave, Opera, and Vivaldi are urged to apply the available fixes promptly. Additionally, CISA has acknowledged active exploitation of CVE-2024-5274 and requested that users patch the flaw before June 18, 2024. It’s crucial for administrators to enable application vulnerability policies and consider setting the severity to high, blocking user access to work data until the app is updated.
Attackers may exploit these vulnerabilities by delivering a maliciously crafted webpage through SMS, email, or messaging platforms, convincing victims to tap the link and initiate the exploit. A successful attack could grant attackers access to sensitive data or deliver phishing sites or malware to the vulnerable device, posing a critical risk to enterprise security postures that rely heavily on mobile devices accessing sensitive cloud data.
OrdrAI CAASM+ (Cyber Asset Attack Surface Management) accelerates the remediation of these threats by providing software version information so you don’t have to wait for vulnerability scans to complete. The most recent zero-day exploits are so serious, the U.S. government has warned federal employees to apply emergency updates or stop using Chrome altogether. Deadlines for updates exist for both June 3rd and June 6th. As with all zero-day vulnerabilities, time-to-remediation is crucial, and OrdrAI enables you to act quickly to secure your assets.
Vulnerability Details:
| CVE-ID | Severity | Details | Exploitability Score | Vector | NVD Published Date |
| CVE-2024-5274 | 8.8 | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 125.0.6422.112 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 2.8 | CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H | 05/28/2024 |
| CVE-2024-4671 | 9.6 | Use after free in Visuals in Google Chrome prior to 124.0.6367.201 allowed a remote attacker who had compromised the renderer process to potentially perform a sandbox escape via a crafted HTML page. | 2.8 | CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:C/C:H/I:H/A:H | 05/14/2024 |
| CVE-2024-4761 | 8.8 | Out of bounds write in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 124.0.6367.207 allowed a remote attacker to perform an out of bounds memory write via a crafted HTML page | 2.8 | CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H | 05/14/2024 |
| CVE-2024-4947 | 8.8 | Type Confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 125.0.6422.60 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code inside a sandbox via a crafted HTML page. | 2.8 | CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H | 05/15/2024 |
| CVE-2024-2886 | Awaiting Analysis | Use after free in WebCodecs in Google Chrome prior to 123.0.6312.86 allowed a remote attacker to perform arbitrary read/write via a crafted HTML page. | Awaiting Analysis | Awaiting Analysis | 03/26/2024 |
| CVE-2024-2887 | Awaiting Analysis | Type Confusion in WebAssembly in Google Chrome prior to 123.0.6312.86 allowed a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code via a crafted HTML page. | Awaiting Analysis | Awaiting Analysis | 03/26/2024 |
| CVE-2024-3159 | 8.8 | Out of bounds memory access in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 123.0.6312.105 allowed a remote attacker to perform arbitrary read/write via a crafted HTML page | 2.8 | CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H | 04/06/2024 |
| CVE-2024-0519 | 8.8 | Out of bounds memory access in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 120.0.6099.224 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. | 2.8 | CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H | 01/16/2024 |
Google Chrome May Vulnerabilities
- CVE-2024-5274 (type confusion in V8 JavaScript and WebAssembly engine)
- CVE-2024-4671 (use-after-free in Visuals)
- CVE-2024-4761 (out-of-bounds write in V8)
- CVE-2024-4947 (type confusion in V8)
Other Google Chrome 2024 Zero-Days
- CVE-2024-2886 (UAF issue in WebCodecs)
- Demonstrated at March hacking contest Pwn2Own Vancouver 2024
- CVE-2024-2887 (type-confusion issue in WebAssembly)
- Demonstrated at March hacking contest Pwn2Own Vancouver 2024
- CVE-2024-3159 (out-of-bounds memory access in V8)
- Demonstrated at March hacking contest Pwn2Own Vancouver 2024
- CVE-2024-0519 (out-of-bounds memory access in Chrome JavaScript engine)
How OrdrAI Helps
OrdrAI CAASM+ integrates with your existing infrastructure utilizing API calls to gather software information from numerous vendors. Further, Ordr’s lightweight, patented script and primary data source, Software Inventory Collector, delivers a high-fidelity software inventory. Then, OrdrAI CAASM+ provides out-of-the-box dashboards to continuously monitor your environment. Correlating all these data sources Ordr provides comprehensive and accurate deduplicated asset visibility, thus preventing exposures.
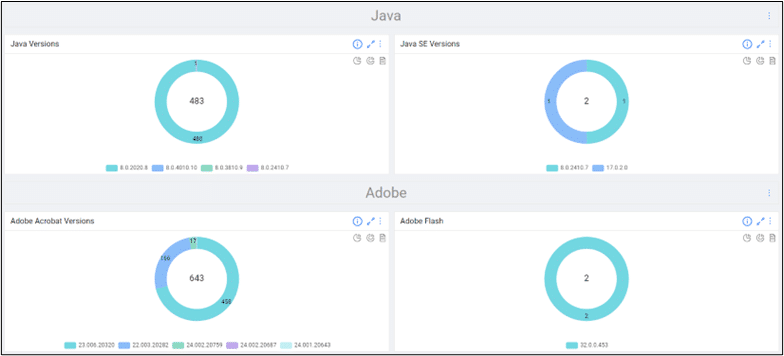
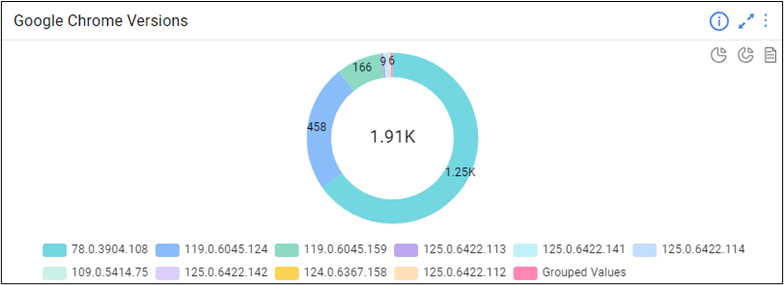
History shows Google Chrome’s recent streak of zero days will repeat itself. Web Browers, Adobe, and Java products have historically been at the top of the list of most vulnerable third-party software. But with OrdrAI CAASM+ you can track all browser versions in your environment.
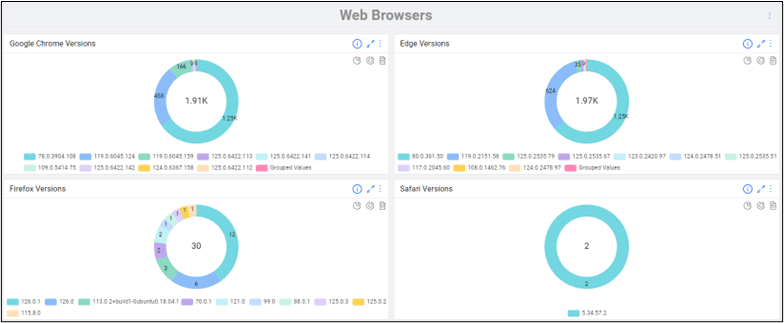
Ordr’s out-of-the-box comprehensive software inventory allows your remediation teams to define scope and begin remediation in just a few clicks, and Identify and track devices with out-of-date browser versions in your environment. With a simple search, you can then add this as a widget and dig deeper into these devices for remediation, identifying the blast radius in case these vulnerabilities are exploited.

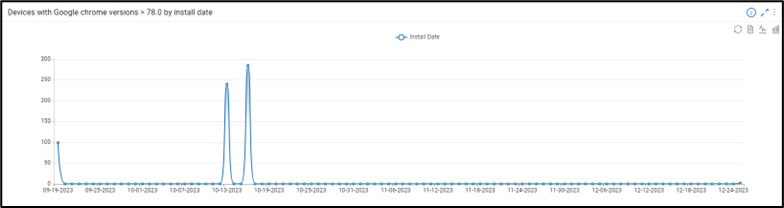
You can also track updates or installation of new browsers based on version number correlated with Install date/Update time.
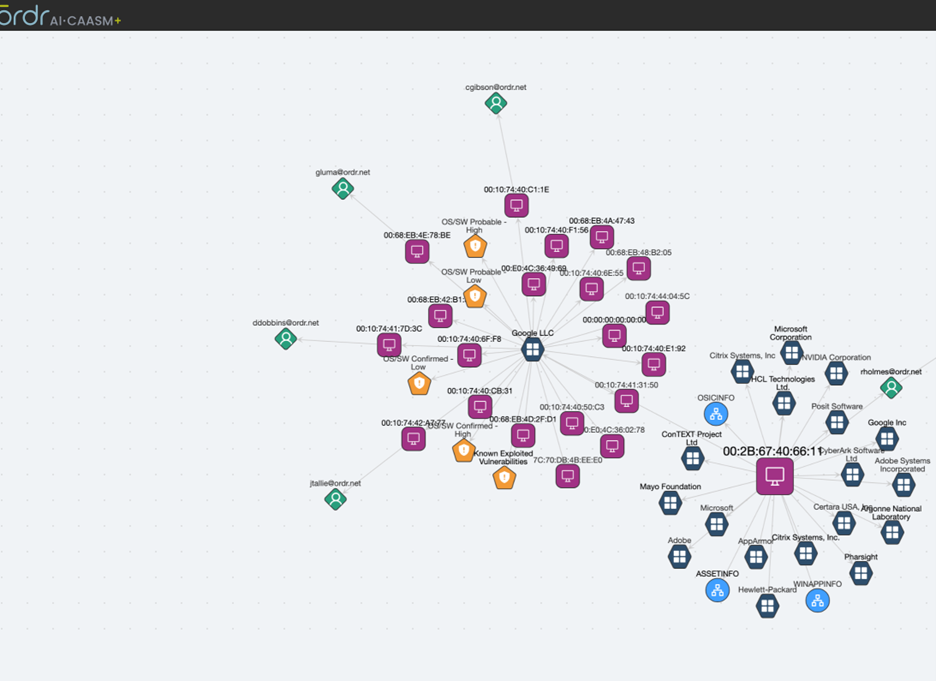
Customers can also get a detailed view of the blast radius via the “Asset Graph” feature, identifying devices, users, and applications associated with a vulnerable asset.
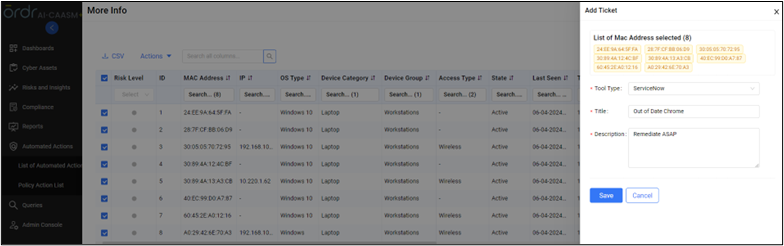
OrdrAI lets you assign a variety of actions to appropriate remediation teams to patch out of date devices.
Actions Supported by OrdrAI CAASM+
OrdrAI CAASM+ allows easy management of vulnerabilities, including assignments and status of the vulnerabilities thanks to deep integration with vulnerability management tools like ServiceNow VR module, providing real-time status updates based on reconciled data.
Furthermore, OrdrAI CAASM+ delivers vital capabilities, like muting or removing a vulnerability from the system when information is not available or is hidden from publicly available dashboards. This is usually done when admins are not ready to patch and are waiting for validation from the manufacturer. OrdrAI also lets you assign vulnerabilities to individual users along with priority and due date. All this information can be shared with CMDB or any other asset management vendors.
Finally, OrdrAI CAASM+ reduces time-to-remediation and risk to the organization with the help of Integration with messaging/collaboration tools and ticketing systems and providing a range of asset specific actions.
OrdrAI CAASM+ is your single source of truth, enabling your teams act with confidence. Contact us for more information.

Interested in
Learning More?
Subscribe today to stay informed and get
regular updates from ORDR Cloud