This security bulletin written with support from ORDR security research analyst Gowri Sunder Ravi
Ransomware attacks have become a critical threat to the healthcare industry, impacting patient care, data security, and disrupting operational continuity. The recent attack on UnitedHealth’s Change Healthcare subsidiary in February 2024 brought to light how attractive the healthcare industry and its data are to hackers. The ALPHV/BlackCat group was behind this attack and received a Bitcoin payment worth $22 million to restore affected data. Another notable threat group targeting the healthcare sector is the Black Basta ransomware gang.
Black Basta has targeted over 500 organizations in the past two years, and healthcare industries are no exception. A joint advisory was issued by the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and Multi-State Information Sharing and Analysis Center (MS-ISAC) detailing the Black Basta threat.
Insights from the Advisory
The alert was issued after a ransomware attack hit major healthcare provider Ascension, affecting the critical services and systems of 140 hospitals in 19 states. Black Basta is regarded as a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) operator, and the group’s attacks have impacted more than 500 organizations and critical infrastructure operators in North America, Europe, and Australia between April 2022 and May 2024 according to the joint advisory. Black Basta has encrypted and stolen data from 12 of 16 critical infrastructure sectors, including the Healthcare and Public Health (HPH) sector.
Like many other members of the ransomware family, Black Basta exploits known vulnerabilities or uses phishing methods to gain initial access. Moreover, the advisory revealed that since February 2024 the group has exploited critical vulnerabilities in the ConnectWise ScreenConnect remote desktop software management application. Similarly, researchers from Trend Micro have linked Black Basta in exploiting CVE-2024-1709, a critical vulnerability with a CVSS score of 10.
Recommendations for Healthcare Organizations:
All organizations and cybersecurity professionals should implement effective cybersecurity measures that align with the Cross-Sector Cybersecurity Performance Goals (CPGs) developed by CISA and NIST. The mitigation tips include the following:
- Update firmware, software, and operating systems to the latest versions as soon as they are released.
- Install modern anti-malware software and update signatures where needed.
- Implement phishing-resistant multi-factor authentication (MFA) across a wide range of services.
- Always validate the URL of the link by hovering the cursor over the link and check if it matches the link’s text.
- Healthcare organizations should ensure that electronic public healthcare information (ePHI) is secured and compliant with HIPAA.
- Organizations must identify their critical business assets by using active scans, passive processes, or a combination of both.
- Identify, evaluate, and prioritize vulnerabilities across the environment so they can be dealt with appropriately within time. For prioritizing vulnerabilities, use the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), which helps decide which vulnerabilities to prioritize.
CISA and NIST also recommend continuous testing of the security program to ensure its optimal performance against the MITRE ATT&CK techniques.
Black Basta – An Overview
Black Basta is a notorious ransomware variant and Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) operator that first appeared in early 2022. According to Malwarebytes, the group was linked with 28 of the 373 confirmed ransomware attacks carried out in April 2024. BlackBasta is believed to have a close affiliation with the Conti ransomware group because of the similarities in their approach to creating malware, leak sites, and communication for payment negotiation and data recovery.
Black Basta has targeted organizations across the globe, including a recent attack on the Toronto Public Library, Canada’s largest public library system, disrupting library services, including access to digital resources, patron information, and other essential functions.

(Image source: hhs.gov)
The group’s primary targets are the English-speaking “Five Eyes” countries of Australia, Canada, New Zealand, United Kingdom, and United States, suggesting a possible political agenda in addition to seeking financial gain. Black Basta use a variety of tools and remote access methods to execute their attacks and exfiltrate data, including Qakbot, SystemBC, Mimikatz, CobaltStrike, and Rclone.
The group employs the double extortion tactic, encrypting the victims’ data, and threatening to publish it online if their demands aren’t met. In early campaigns, Black Basta used email or spear phishing methods to get initial access to a target organization and deploy ransomware on their devices. The gang has also used other techniques to deploy ransomware, like disabling the compromised system DNS to complicate the recovery process and deploying ransomware that targets Linux-based VMware ESXi Virtual Machines (VMs). They have a public leak website where they publish data about their victims and samples of stolen data to create pressure to pay ransom.
Despite its success and widespread impact, Black Basta maintains a low profile, operating similarly to private threat groups like Conti, TA505, and Evil Corp. The group’s modus operandi is to conduct a careful assessment of an intended target before conducting a focused attack. This sets them apart from threat actors that conduct broader, less selective campaigns.
How ORDR Helps
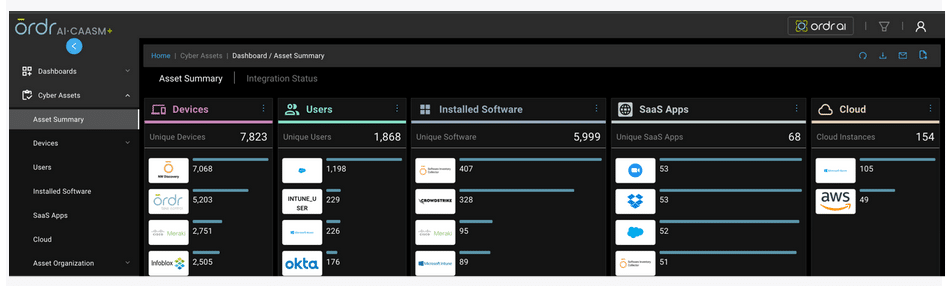
Organizations are increasingly exposed to cyber threats like ransomware attacks without even knowing about them, mainly because the enterprise attack surface continues to expand making it challenging for security teams to correlate asset data across multiple sources to identify security gaps, prioritize vulnerabilities, and remediate threats. Fortunately, ORDRAI Protect and the recently launched ORDRAI CAASM+ solutions provide comprehensive and accurate deduplicated asset visibility, thus preventing exposures.
SEE:
ORDRAI automatically discovers, classifies, and profiles all devices based on the manufacturer, make, and model, while providing a granular view of data flows and asset attributes associated with all the devices in your environment.
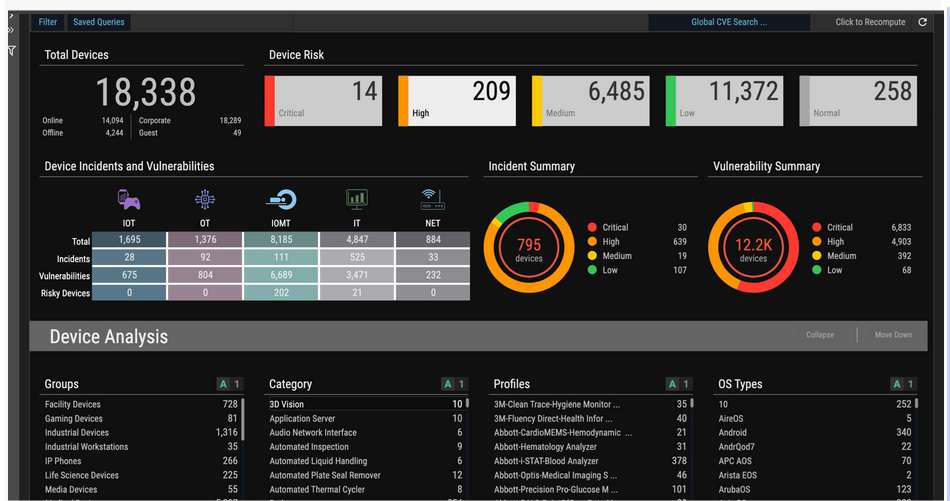

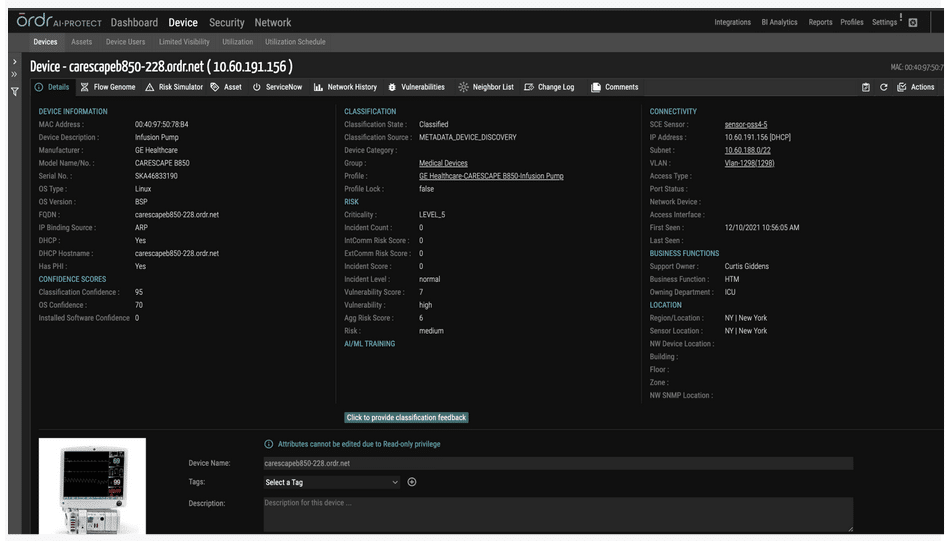
ORDRAI correlates and deduplicates all asset data (Including users, installed applications, IoT and IoMT, OT, cloud services, and more) across multiple sources, then classifies and profiles all devices based on the manufacturer, make, model, and other information pulled from integration sources.
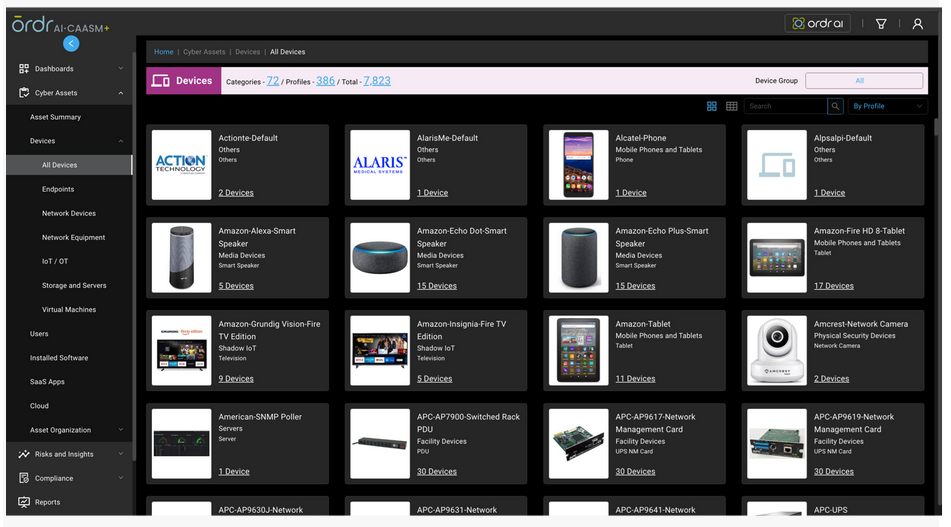

KNOW:
ORDRAI ‘s external IP/IOC detects and tracks asset communication to prohibited IP/URLs in real-time:
- ORDR provides in-depth insights into category traffic analysis that highlights the communication patterns between devices and external entities, making it easier to identify devices communicating to a list of prohibited countries or any group of IPs that customers want to monitor that are associated with popular threat actors.
- ORDR uses a continuously updated cloud-based threat intelligence platform, and all communications are marked accordingly in the ORDR Security Threat Card.
- ORDR has an IDS engine that can detect attacks associated with techniques used by Black Basta and generate alerts based on analysis of packets transacting over the wire.
- ORDR also provides the capability to baseline all communications based on profile, location, business function, or any customized entity using our AI/ML techniques.
- ORDR detects anomalies based on any deviations observed for this traffic.
ORDRAI uses multiple methods to collect and deduplicate the vulnerability data from multiple sources and provide an easy way to manage the vulnerabilities.
- Conducts analyses based on data collected using passive and active techniques, make, model, manufacturer, OS, and from integration with vulnerability assessment systems like Rapid7, Tenable, and Qualys. This works for assets that can withstand scan and are scanned regularly.
- ORDRAI Software Inventory Collector is a lightweight script that detects based on KB/HF correlation instead of scanning the asset for vulnerabilities. This works great for assets that cannot withstand scans, and for assets that are not updated regularly.
- ORDRAI uses known exploitable vulnerability (KEV) data and the Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS) to provide additional context to the vulnerabilities based on the real-world data.
- ORDRAI provides additional context to assets with vulnerabilities, including normalizing risks based on classification, allowing users to modify risk scores based on asset criticality.
Based on vulnerability info collected by these methods, ORDRAI customers can get an accurate assessment of risks in their environment, including:
- Risk summary that dashboard delivers a high-level risk map of the organization making it easy for security teams to track gaps and vulnerabilities in their environment.
- A clear view of security gaps present in the organization via a “Security Control Gaps” dashboard highlighting devices without EDR Installed, MDM Installed, and devices not scanned by vulnerability scanners.
- A vulnerability dashboard that provides a complete “state of the union” on vulnerabilities affecting the organization.
- Compliance dashboards that provide a snapshot of non-compliant assets present in your environment.
- A query builder for creating custom dashboards or querying information based on customer needs.
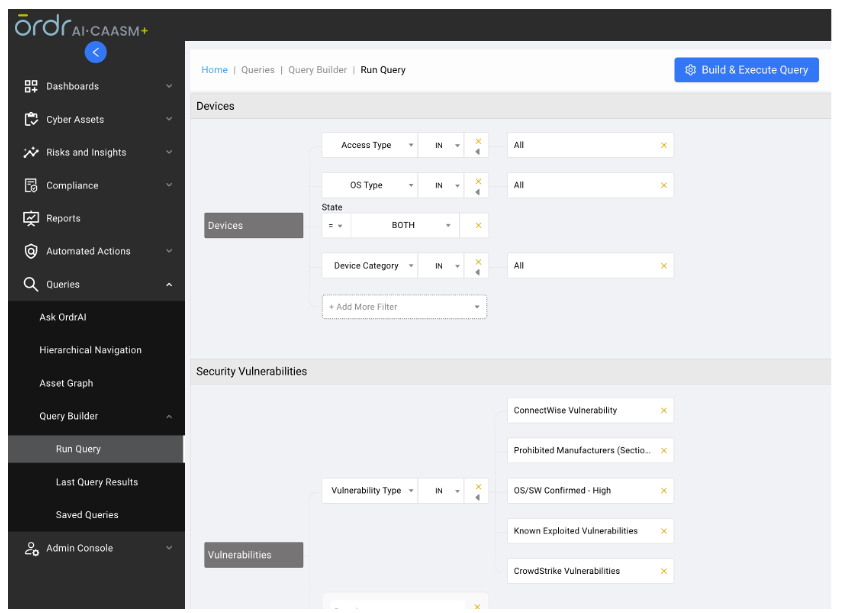
- Ask ORDRAI for instant info on assets, vulnerabilities, coverage gaps, and user risk.

Customers can also get a detailed view of the blast radius via the “Asset Graph” feature, identifying devices, users, and applications associated with a vulnerable asset.
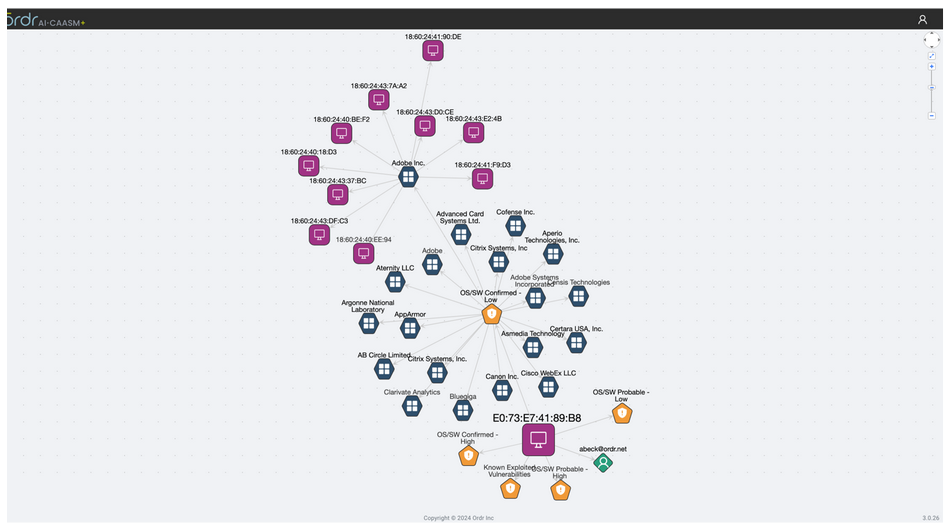
SECURE:
ORDRAI allows easy management of vulnerabilities, including assignments and status of the vulnerabilities, thanks to deep integration with vulnerability management tools like ServiceNow VR module, providing real-time status updates based on reconciled data. That delivers vital capabilities, including:
- Muting or removing a vulnerability from the system when information is not available or is hidden from publicly available dashboards. This is usually done when admins are not ready to patch and are waiting for validation from the manufacturer.
- Ability to assign vulnerabilities to individual users along with priority and due date. All this information can be shared with CMDB or any other asset management vendors.
- ORDRAI Protect also allows you to clear and mute incidents in addition to vulnerability related actions.
ORDRAI supports a variety of additional actions like
- Network based enforcement for reactive rapid threat containment (Change VLAN, Shutdown Port, Integrate with Firewall) for quarantining affected devices and limiting communications over certain protocols.This automation works with almost any networking, switch, or wireless controller vendor.
- Integration with ticketing system, messaging, and collaboration tools.
- ORDR segmentation add-on to enable segmentation of impacted devices, limiting access to only must-have communications based on Zero Trust policies.
Are you ready to learn more about ORDR products and how they can reduce the likelihood of ransomware attacks? Schedule a demo now!
Helpful links:

Interested in
Learning More?
Subscribe today to stay informed and get
regular updates from ORDR Cloud